Your basket is currently empty!

Leveraging Approvals and Market Access with CE-Marking
Leveraging EU MDR CE Marking for Global Medical Device Market Access
A comprehensive guide to maximizing your regulatory strategy through EU MDR compliance
Introduction
Navigating the complex landscape of medical device regulatory affairs can be challenging for manufacturers seeking global market access. While many companies view regulatory compliance as merely a hurdle to overcome, strategic manufacturers recognize that securing EU MDR CE-marking can serve as a powerful gateway to multiple international markets.
This article explores how medical device manufacturers can leverage European certification to streamline their global regulatory strategy, reducing time-to-market and compliance costs while maximising market opportunities.
Understanding EU MDR CE Marking
The European Medical Device Regulation (MDR) represents one of the most rigorous regulatory compliance frameworks in the world. Devices that successfully navigate this system demonstrate adherence to stringent safety, performance, and quality standards. CE-marking under the MDR indicates that a product meets all applicable requirements and can be legally marketed throughout the European Economic Area (EEA).
The MDR’s comprehensive approach encompasses:
- Thorough risk management in medical devices
- Robust clinical evaluation reports
- Comprehensive post-market surveillance
- Rigorous quality management systems
These demanding requirements explain why many global regulatory bodies recognise or partially accept EU MDR certification as evidence of compliance.
Global Recognition of CE-Marking
Many countries have developed regulatory systems that acknowledge CE-marking, either through formal recognition programs or simplified approval pathways. This strategic approach allows manufacturers to use their EU regulatory investment as a springboard to global markets.
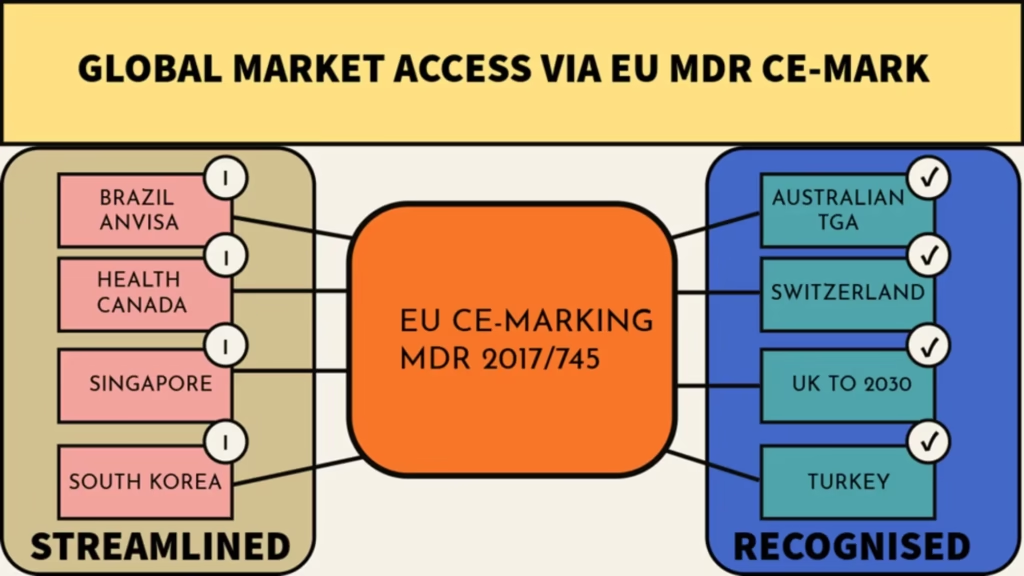
Markets with Formal Recognition of CE-Marking
Several jurisdictions have established formal recognition mechanisms for CE-marked medical devices:
Australia (TGA)
The Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) offers the Comparable Overseas Regulator (COR) pathway, which can substantially streamline registration for CE-marked devices. This approach allows manufacturers to leverage their existing conformity assessment data rather than duplicate efforts. Given that formal certification through the TGA via the Conformity Assessment Certificate (CAC) has a similar time/cost to obtaining EU CE-marking, the strategic choice is to pursue MDR compliance and leverage this in Australia.
Switzerland
While not an EU member, Switzerland maintains a Mutual Recognition Agreement (MRA) with the EU, allowing mutual acceptance of conformity assessments. CE-marked devices can typically be marketed in Switzerland with minimal additional requirements. These additional requirements can include appointing a Swiss Authorized Representative (for non-Switzerland-based manufacturers) and registering the device with Swissmedic.
United Kingdom
Following Brexit, the UK was considered a third-country outside the EU, and recently established the UKCA marking system. However, during the ongoing transitional period, the UK continues to recognize CE marking for most medical devices, with a staged approach to full UKCA implementation. This is expected to continue until 2030 for some device classes, meaning that CE-marking continues to be an attractive market entry option in the medium term.
Turkey
The Turkish regulatory system closely mirrors the EU MDR. CE-marked devices typically face simplified registration processes for the Turkish market.
Markets with Streamlined Pathways for CE-Marked Devices
Many other countries don’t formally recognize CE marking but offer expedited review processes for devices already certified in Europe:
Brazil (ANVISA)
Brazil’s regulatory authority accepts certain aspects of EU technical documentation, potentially reducing registration timelines for CE-marked devices.
Canada (Health Canada)
While CE-marking certificates for devices do not allow simplified approvals in Canada, the Medical Device Single Audit Program (MDSAP) facilitates acceptance of quality management system audits across multiple jurisdictions, including Europe and Canada.
Singapore
Singapore’s Health Sciences Authority (HSA) offers expedited evaluation routes for products with prior approval from reference regulatory agencies, including European Notified Bodies.
South Korea
The Korean Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) maintains agreements with European authorities that can reduce documentation requirements for certain device classes.
Strategic Benefits of Leading with EU MDR Compliance
Prioritizing EU MDR certification as the cornerstone of a global regulatory strategy offers several advantages:
1. Comprehensive Technical Documentation
The MDR’s Technical Documentation requirements are among the most comprehensive globally. Meeting these standards typically means manufacturers have addressed most elements needed for other markets.
2. Risk-Based Approach
The MDR’s emphasis on risk management in medical devices aligns with international best practices reflected in ISO 14971 and similar standards worldwide.
3. Clinical Evidence Standards
The rigorous clinical evidence requirements under MDR often exceed those of other markets, meaning manufacturers who satisfy European demands typically have sufficient data for other jurisdictions.
4. Post-Market Surveillance Systems
The MDR’s advanced post-market surveillance framework prepares manufacturers for vigilance requirements across global markets.
Implementing a CE-Focused Global Strategy
For manufacturers seeking to leverage CE-marking for international access, consider the following approach:
- Design for MDR compliance from the start
Build product development processes with EU requirements as the baseline, ensuring technical files meet or exceed European standards. - Select Notified Bodies with global recognition
Partner with European Notified Bodies whose certifications carry maximum weight with other regulatory authorities. - Harmonize quality management systems
Implement quality systems that satisfy multiple regulatory frameworks, potentially incorporating MDSAP principles. - Develop modular technical documentation
Create documentation packages that can be easily adapted for different markets while maintaining a consistent core based on MDR requirements. - Establish comprehensive clinical evaluation processes
Develop robust clinical evaluation reports that can satisfy diverse global requirements.
Challenges and Considerations
While leveraging CE-marking offers significant advantages, manufacturers should consider:
- Divergent requirements for labelling and instructions for use
- Varying classification systems across jurisdictions
- Local language requirements and country-specific representation needs
- Evolving regulatory landscapes requiring continuous monitoring
- Potential for regulatory divergence between the EU and other markets over time
Conclusion
For forward-thinking medical device manufacturers, EU MDR compliance represents not just a requirement for European access but a strategic foundation for global market entry. By approaching regulatory affairs with this perspective, companies can optimize resources, reduce redundancy, and accelerate international expansion.
Investing in comprehensive medical device regulatory training and developing expertise in European medical device regulations provides returns beyond the European market. This approach transforms compliance from a cost centre into a strategic advantage, opening doors to multiple markets with a single, albeit rigorous, regulatory effort.
Leave a Reply